Understanding What is Dry for Wheat: A Comprehensive Guide
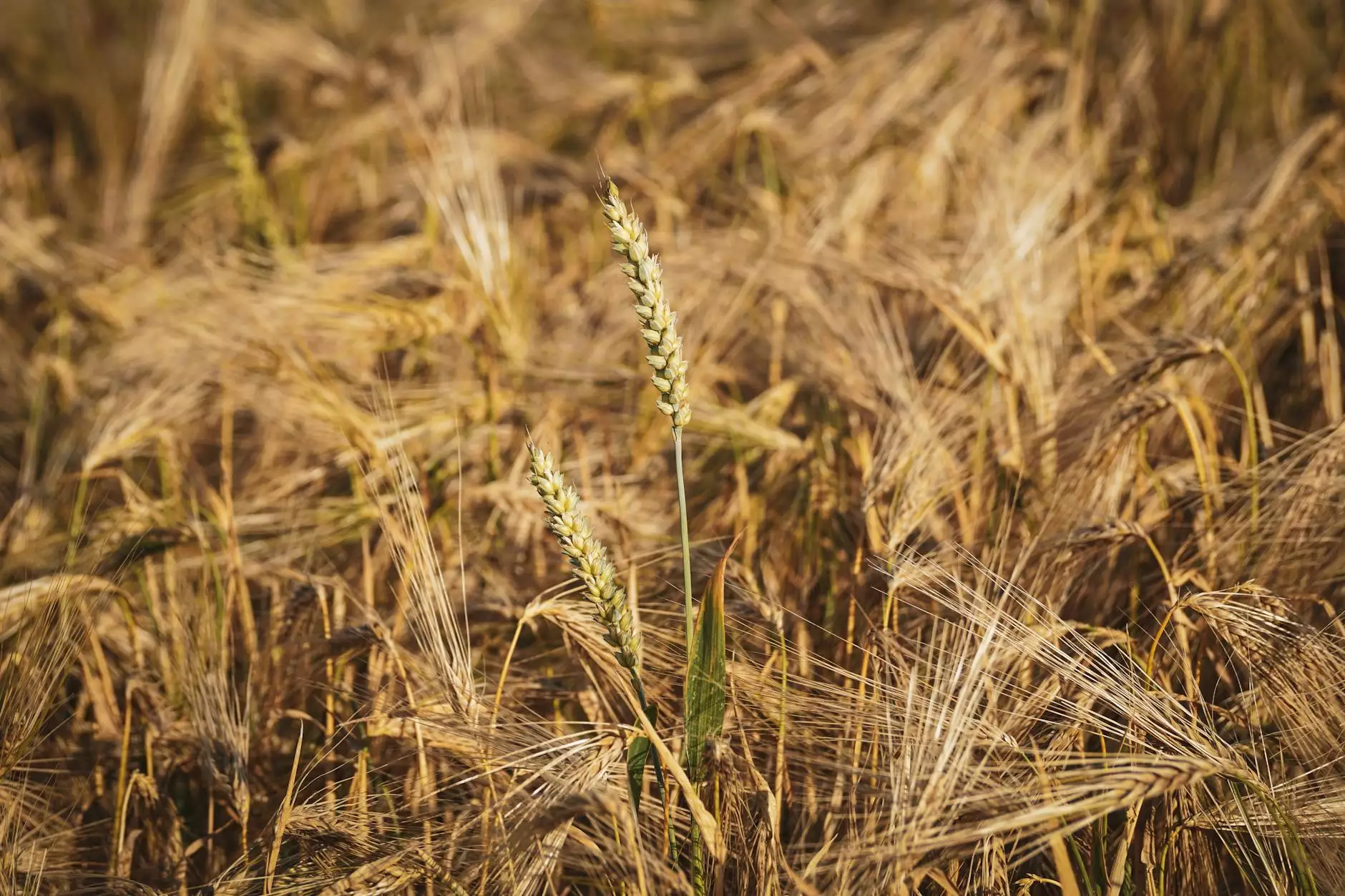

The cultivation of wheat is a delicate balance between moisture levels and dry conditions. When farmers refer to "what is dry for wheat," they are discussing the ideal moisture conditions necessary for the wheat crop to thrive. In this detailed article, we will explore this concept covering various aspects such as farming techniques, equipment maintenance, and how to manage wheat crops effectively in dry conditions.
1. The Importance of Moisture in Wheat Cultivation
Moisture plays a pivotal role in wheat farming. Adequate water supply is essential during different growth stages, from germination to harvesting. Understanding what is dry for wheat is crucial for farmers to manage their resources efficiently.
1.1 How Moisture Affects Wheat Growth
Wheat requires a balanced amount of moisture. The following points highlight the significance of moisture in wheat growth:
- Germination: Seeds absorb moisture to initiate germination. Too much or too little moisture can hinder this process.
- Vegetative Growth: Young wheat plants need consistent watering to grow strong and healthy.
- Flowering: At the flowering stage, water stress can significantly affect the yield, as it impacts pollination.
- Maturity: Adequate moisture is necessary before harvest to ensure grain filling is completed.
2. Understanding Dry Conditions
Dry conditions for wheat can be defined as periods where soil moisture levels drop below optimal requirements. It’s crucial to know how to interpret these conditions.
2.1 Characteristics of Dry Conditions
In an agricultural context, what is dry for wheat can be characterized by:
- Soil Moisture Levels: Ideal soil moisture levels for wheat should generally be between 20% to 25%. Levels below this can be categorized as dry.
- Weather Patterns: Extended periods without rainfall and high temperatures exacerbate dry conditions.
- Crop Stress: Visible signs of stress in wheat, such as wilting or discoloration, are indicators of dry conditions.
3. Impact of Dry Conditions on Wheat Yields
Understanding how dry conditions impact yields is vital for effective crop management. Here we analyze the effects:
3.1 Yield Reduction
Dry conditions can lead to:
- Smaller Grain Size: Insufficient moisture results in smaller and lower-quality grains.
- Reduced Kernel Count: Low water availability during critical growth phases leads to fewer kernels per head.
- Negative Effects on Quality: Grain quality suffers, leading to lower market prices.
4. Strategies to Manage Dry Conditions
Farmers can adopt several strategies to mitigate the effects of dry conditions on wheat crops.
4.1 Irrigation Techniques
Irrigating wheat crops is one of the most effective ways to combat dry conditions. Here are some methods:
- Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation.
- Sprinkler Systems: A more conventional method, however, may increase water loss due to evaporation.
4.2 Soil Conservation Practices
Improving soil health is vital in retaining moisture:
- Cover Cropping: Use cover crops to enhance soil structure and retain moisture.
- No-Till Farming: Reducing tillage helps in maintaining soil moisture levels.
4.3 Crop Rotation
Implementing crop rotation can improve soil health and moisture retention:
- Diverse Crops: Rotating wheat with crops that have different moisture requirements can help the soil recover!
- Legumes: Incorporating legumes into the rotation can enrich nitrogen levels, improving overall soil health.
5. The Role of Farming Equipment in Managing Dry Conditions
The efficiency of farming equipment plays a critical role in mitigating the challenges posed by dry conditions.
5.1 Maintenance of Equipment
Regular maintenance of farming equipment is essential to ensure optimal performance:
- Checking Irrigation Systems: Regular checks on irrigating equipment can prevent breakdowns during critical periods.
- Calibration of Spray Equipment: Proper calibration ensures that water is applied evenly and efficiently.
5.2 Investment in Technology
Utilizing advanced technology can also combat the impact of dry conditions:
- Soil Moisture Sensors: These sensors provide real-time data about soil moisture levels, allowing for precise irrigation.
- Weather Tracking Software: Applications that forecast weather patterns help farmers plan their activities accordingly.
6. Conclusion
Understanding what is dry for wheat is crucial for any farmer focused on maximizing yields and ensuring sustainable practices. By recognizing the signs of dry conditions and implementing effective moisture management strategies, farmers can better prepare and adapt to changes in weather patterns. The combination of innovative farming practices, proper equipment maintenance, and a solid understanding of crop requirements can lead to successful wheat farming, even in challenging dry conditions. At TSGC Inc., we specialize in farm equipment repair and provide top-notch farming equipment to support your agricultural needs. Your success is our mission!